Diamond Guide
Basics of a Diamond - The 4 Cs
The 4Cs stand for Carat, Colour, Clarity and Cut. Diamonds are graded in each of these areas. Taken collectively, those grades determine a diamond’s value.
Carat
Carat weight has the most influence on diamond value. Diamonds of different shapes may appear different sizes for the same carat weight. The weight or size of a diamond is measured in carats (ct.).One carat weighs 1/5 of a gram and is divided into 100 points, so a diamond weighing 1.07 ct. is referred to as “one carat and seven points.
Diamond Carat Charts
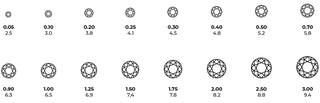
It is important to note that diamonds of the same weight don’t necessarily have the same size appearance. Those cut too shallow or deep may look small for their weight, or suffer in brilliance
Colour
Most of the world’s diamonds are graded on a scale of colourless to light yellow or light brown. Other hues are graded on a different scale, and called Fancy Coloured Diamonds.
Most diamonds of gem quality used in jewellery vary in shade from completely colourless down to a visible yellow or brown tint. The rarest and most expensive are diamonds in the colourless range graded D,E and F on a scale that descends to Z.
As diamond size increases, colour becomes more noticeable. This is especially important to keep in mind if you are purchasing a diamond of two carats or greater.

Clarity
Clarity evaluates a diamond’s freedom from internal and external clarity characteristics which occurred during formation, polishing, or wear and tear.
Since diamonds form under extreme heat and pressure, internal and external characteristics are common. There are two types of clarity characteristics: inclusions and blemishes.
In order to grade the clarity of a diamond, it is necessary to observe the number and nature of external and internal characteristics of the stone, as well as their size and position. The difference is based on their locations: inclusions are enclosed within a diamond, while blemishes are external
characteristics.
Diamond Clarity Chart
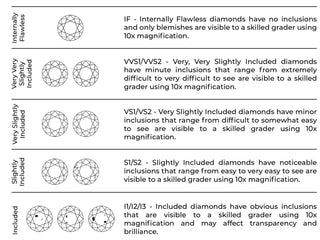
Cut
The cut of a diamond includes everything humans did to convert it from a rough crystal to a polished gemstone capable of brightness, fire, contrast and
scintillation.
While nature determined the colour and clarity of a natural diamond, man is responsible for the cut quality which brings it to life. The planning,
proportions, cutting precision, and details of the finish determine how brilliant, dispersive, and scintillating the diamond will be.
The most popular diamond in the age of modern electric lighting is the Round Brilliant.

The right cut will enhance the sparke and the scintillation of the diamond. The better the cut, the more likely your diamond is to sparkle bright and look gorgeous!
